
HL Paper 3
Explain, in terms of their bonding, how the presence of oxygen and ozone in the ozone layer helps to prevent both higher and lower energy UV light from reaching the surface of the Earth.
Markscheme
bonds in oxygen are double and bonds in ozone are (intermediate) between single and double;
bonds in oxygen are stronger / bonds in ozone are weaker;
oxygen absorbs higher energy UV light / ozone absorbs lower energy UV light;
Examiners report
Although part (a) was generally well answered, many candidates missed the first mark through failing to refer to bonds in both oxygen and ozone.
Ozone is a gas present in both the stratosphere and the troposphere.
Oxygen absorbs much of the ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, but ozone is important because it absorbs UV radiation not absorbed by oxygen. Explain, referring to the bonding in the two molecules, why this is the case.
Markscheme
oxygen has double bond/bond order 2;
ozone has delocalized bond/bond order 1.5;
oxygen bond/bond in oxygen (molecule) is stronger/shorter / ozone bond is weaker/longer;
ozone absorbs light of lower energy/lower frequency/longer wavelength;
Accept suitable diagram.
Examiners report
Most candidates were aware of the difference in bonding between diatomic oxygen and ozone, and the effect this has on the UV frequencies they absorb.
(a) (i) Explain the dependence of the dissociation of diatomic oxygen, O2, and ozone, O3, on the wavelength of light.
(ii) State the equations for the formation and depletion of ozone in the stratosphere by natural processes.
Formation of ozone:
Depletion of ozone:
(b) (i) State the equations for the depletion of ozone by the CFC, dichlorodifluoromethane, CCl2F2.
(ii) Use your answer to part (b) (i) to explain why CFCs are so effective at ozone depletion.
Markscheme
(a) (i) shorter wavelength/higher energy radiation/UV is needed to break the bond in \({{\text{O}}_2}\);
because \({{\text{O}}_2}\) has double/stronger bond;
Accept converse argument for O3.
(ii) Formation of ozone:
\({{\text{O}}_2} \to {\text{2O}} \bullet \) and \({{\text{O}}_2} + {\text{O}} \bullet \to {{\text{O}}_3}\);
Allow mark for second equation only.
Depletion of ozone:
\({{\text{O}}_3} \to {{\text{O}}_2} + {\text{O}} \bullet \) / \({{\text{O}}_3} + {\text{O}} \bullet \to {\text{2}}{{\text{O}}_2}\);
Ignore state symbols.
Allow radical representation without dot throughout.
Do not allow inconsistent use of dot symbol.
(b) (i) \({\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_2}{{\text{F}}_2} \to {\text{CCl}}{{\text{F}}_2} \bullet + {\text{Cl}} \bullet \);
\({\text{Cl}} \bullet + {{\text{O}}_3} \to {\text{ClO}} \bullet + {{\text{O}}_2}\);
\({\text{ClO}} \bullet \to {\text{Cl}} \bullet + {\text{O}} \bullet \);
\({\text{ClO}} \bullet + {\text{O}} \bullet \to {{\text{O}}_2} + {\text{Cl}} \bullet \);
Ignore state symbols.
Allow radical representation without dot throughout.
Do not allow inconsistent use of dot symbol.
(ii) \({\text{Cl}} \bullet {\text{/Cl}}\) regenerated / OWTTE;
can deplete further ozone molecules / catalytic / OWTTE;
Examiners report
At HL, it was very surprising and disappointing that candidates did not do well on this question as many of the questions were based on core chemical principles applied in an environmental context. Candidates could not usually relate the strength of the oxygen to oxygen bond in ozone versus that in oxygen to energy needed to break the bond.
Some of the better candidates mentioned bond order and supported their answer with well represented diagrams. In (ii), many candidates were able to state at least one equation for either the formation or depletion of ozone, though many were not consistent with the use of the dot symbol to represent the radical. Radicals can be represented with or without a dot, but it is important that candidates are consistent in whatever representation they use. In (b), many candidates were not able to write the equations for the depletion of ozone by CFC, and only a small minority scored all three marks here. In addition, it was very disappointing that candidates could not explain why CFCs are so effective at ozone depletion.
Ozone prevents UV radiation emitted from the Sun reaching the surface of the Earth.
Explain, with the aid of Lewis (electron-dot) structures, the difference between oxygen and ozone in terms of the energy required to dissociate both molecules.
Oxygen: Ozone:
One CFC, Freon-13 (chlorotrifl uoromethane), which can be used as a refrigerant, has been phased out by the Montreal Protocol. Describe, using equations, the mechanism of the catalysis of ozone depletion by this particular CFC.
Markscheme
Oxygen: correctly drawn Lewis structure and Ozone: correctly drawn Lewis structure;
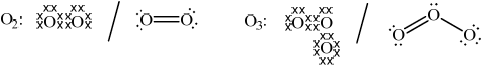
Allow any combination of dots, x’s or lines to represent electron pairs.
Allow representation of two resonance structures for ozone.
oxygen has a higher bond order than ozone and oxygen needs more energy to dissociate / OWTTE;
Exact bond orders of 2 for oxygen and 1.5/1 and 2 for ozone may be given for first statement in M2.
Do not award M2 if incorrect bond orders are stated for either species.
\({\text{C}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{Cl (}} + {\text{UV/}}hf{\text{/}}hv{\text{)}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}} \bullet + {\text{Cl}} \bullet \);
\({\text{Cl}} \bullet + {{\text{O}}_3} \to {\text{ClO}} \bullet + {{\text{O}}_2}\);
\({\text{ClO}} \bullet + {{\text{O}}_3} \to {\text{Cl}} \bullet + {\text{2}}{{\text{O}}_2}\);
Accept \(ClO \bullet + O \bullet \to {O_2} + Cl \bullet \) for M3.
Allow representation of radicals without \( \bullet \) if consistent throughout.
Penalize inconsistency of radical representations once only in E16.
Examiners report
(a) and (b) were well answered though the weaker students in (b) simply stated that \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{6}}}\) contains no chlorine – no credit was awarded for this. (c) (i) was generally well done though temperature inversion often was not correctly described. Part (ii) was very poorly answered and most only scored one mark. PANs continue to be a real challenge for candidates and similar to previous examination papers candidate performance here was very poor. In (d) the most common mistake was the sight of two lone pairs instead of one on the central oxygen in ozone. (e) was well done however, though some inconsistency of radical symbols was common.
(a) and (b) were well answered though the weaker students in (b) simply stated that \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{6}}}\) contains no chlorine – no credit was awarded for this. (c) (i) was generally well done though temperature inversion often was not correctly described. Part (ii) was very poorly answered and most only scored one mark. PANs continue to be a real challenge for candidates and similar to previous examination papers candidate performance here was very poor. In (d) the most common mistake was the sight of two lone pairs instead of one on the central oxygen in ozone. (e) was well done however, though some inconsistency of radical symbols was common.